Understanding Glycated Hemoglobin: Definition and Significance
So, what is glycated hemoglobin exactly? Simply put, it’s hemoglobin with sugar attached to it. This happens when glucose in the blood attaches itself to the hemoglobin in red blood cells. The test provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over about three months. It’s a simplified way of understanding long-term glucose management. Using glycohemoglobin a1c tests is essential for anyone with diabetes, as it helps set clear goals for maintaining blood sugar at healthy levels, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes-related issues.
Breaking Down the A1C Test Procedure
Before the Test
Preparation for the test is minimal. There’s no need for fasting or any special diet beforehand. Just knowing when the appointment is scheduled is critical.
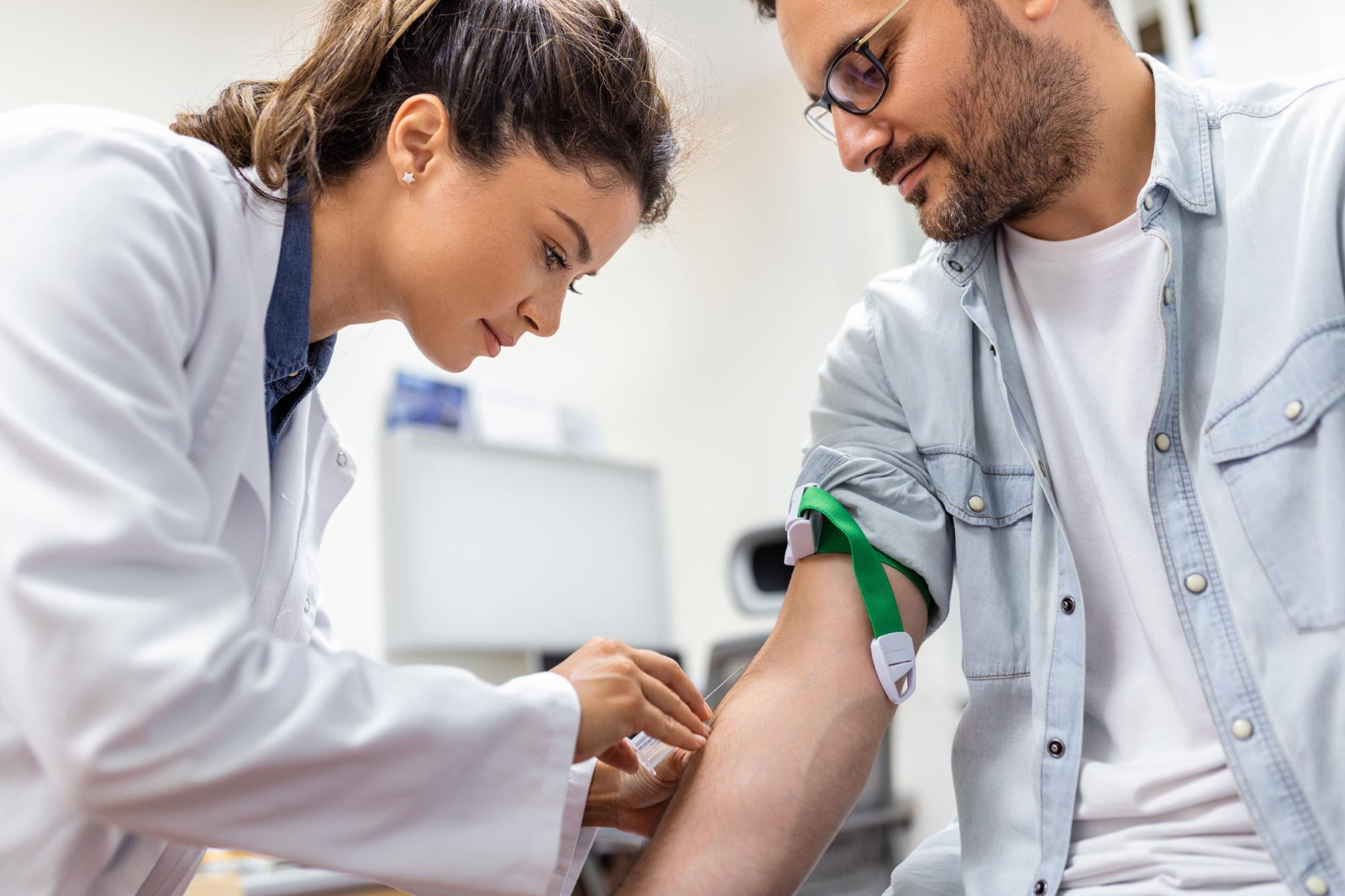
During the Test
Expect a simple procedure. A healthcare professional will collect a small sample of blood, usually from a vein in your arm. The process is quick and relatively painless.
After the Test
Once the sample is collected, it is sent to a lab where the glycated hemoglobin assay takes place. Results are usually available within a few days. Once available, your doctor will discuss them with you to help you understand your current diabetes management status.
Decoding A1C Results and Implications for Lifestyle
When you get your A1C results, they come as a percentage. The glycated hemoglobin meaning behind these percentages? Lower numbers indicate better control over your blood sugar in recent months. Typically, an A1C below 7% is a common target, although it can vary. Diet, particularly a traditional Indian diet rich in carbohydrates, can influence these results. Adjustments might be necessary for some people, based on their personal health goals. Understanding what your A1C result means can guide necessary lifestyle changes, making the understanding of glycated hemoglobin explained incredibly empowering.
Debunking Myths About the A1C Test
There are several myths floating around about the A1C test. One major misconception is that it can replace daily blood glucose testing, but both are needed for thorough diabetes management. Misunderstanding this can lead to poor health decisions. Another myth is that consuming sugar alone significantly alters results. In reality, consistent overall diet and lifestyle matter more. Dispelling these myths is important for accurate disease management.
Lifestyle Modifications and Strategies to Improve A1C Levels
Indian dietary habits, rich in carbs, often affect glucose management. However, several strategies can improve A1C levels:
- Plan meals: Opt for balanced eating by including more vegetables and fibers.
- Physical activity: Engage in at least 30 minutes of exercise daily.
- Manage stress: Practice mindfulness or yoga, focusing on relaxation.
Take inspiration from real-life success stories. For instance, someone might find their glycated hemoglobin explained in a breakthrough moment, leading them to embrace walking and adjusting their diet, resulting in healthier A1C levels.
Impact of A1C Levels on Diabetes Complications
Low A1C levels usually mean better diabetes control, which minimizes the risk of complications like heart disease, kidney problems, or neuropathy. Keeping A1C within a healthy range is crucial. Not only does it ensure a better quality of life, but it also prevents long-term health issues that might arise from uncontrolled diabetes.
Testing Frequency: Regular Monitoring for Optimal Health
For optimal health management, it’s advised that the A1C test is conducted at least twice a year. For individuals struggling to meet their goals, more frequent testing might be necessary. This routine check helps keep an eye on diabetes management and adjust medications or lifestyle as needed.
Emotional Response and Psychological Coping with A1C Results
Receiving unexpected A1C results can be emotionally challenging. It’s normal to feel worried or disappointed. However, addressing these feelings is important. Maintaining a positive mindset and seeking support from mental health professionals can be beneficial in coping with the emotional aspects of diabetes management.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Diabetes Management
Comprehending the glycated hemoglobin and how it impacts diabetes management allows individuals to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment plans. With the right support and resources, anyone can take control of their diabetes management. Regular A1C testing and understanding its meaning can provide the foundation for effective strategies.
Additional Resources for Diabetes Management
For further reading and support, consider reaching out to Indian diabetes associations. These organizations can provide helpful resources and connectivity to support networks. Additionally, exploring strategies tailored to the Indian lifestyle can help in better diabetes management.